As the world continues its journey towards a sustainable and greener future, solar photovoltaic (PV) systems have emerged as a shining star in the renewable energy landscape. These systems come in various configurations, designed to maximize energy production in specific scenarios. Understanding the types of systems available and the best one for your home can be overwhelming and confusing. To help you better understand what’s the best solution for your home, we’ve laid them out here for you.
To understand what’s best for your home, you have to understand the significance of the inverter for your solar PV system.
Inverter Technology
- Alternating Current (AC) electricity is used in the home, Solar Panels create Direct Current (DC) electricity
- Inverters convert Direct Current to Alternating Current
- Inverters create clean energy from the sun that feeds directly into your electrical panel
There are three main types of Inverter technologies:
Let’s explore their differences, benefits, and applications to help you make an informed choice for your solar energy journey!

-
String Inverters: The Tried and True Technology
String inverters have long been a staple in the solar industry. They connect multiple solar panels in series (or strings) and convert the DC power generated by these panels into AC power suitable for your home or the grid.
String inverters have their own set of advantages:
 Cost-Effective: String inverters are typically more affordable and easier to install, making them a popular choice for larger PV installations.
Cost-Effective: String inverters are typically more affordable and easier to install, making them a popular choice for larger PV installations.- Proven Technology: String inverters have a track record of reliable performance, making them a dependable option for residential and commercial applications.
- Centralized Monitoring: While not as precise as panel-level monitoring, string inverters offer centralized system monitoring to keep tabs on your overall energy production.
Disadvantages are:
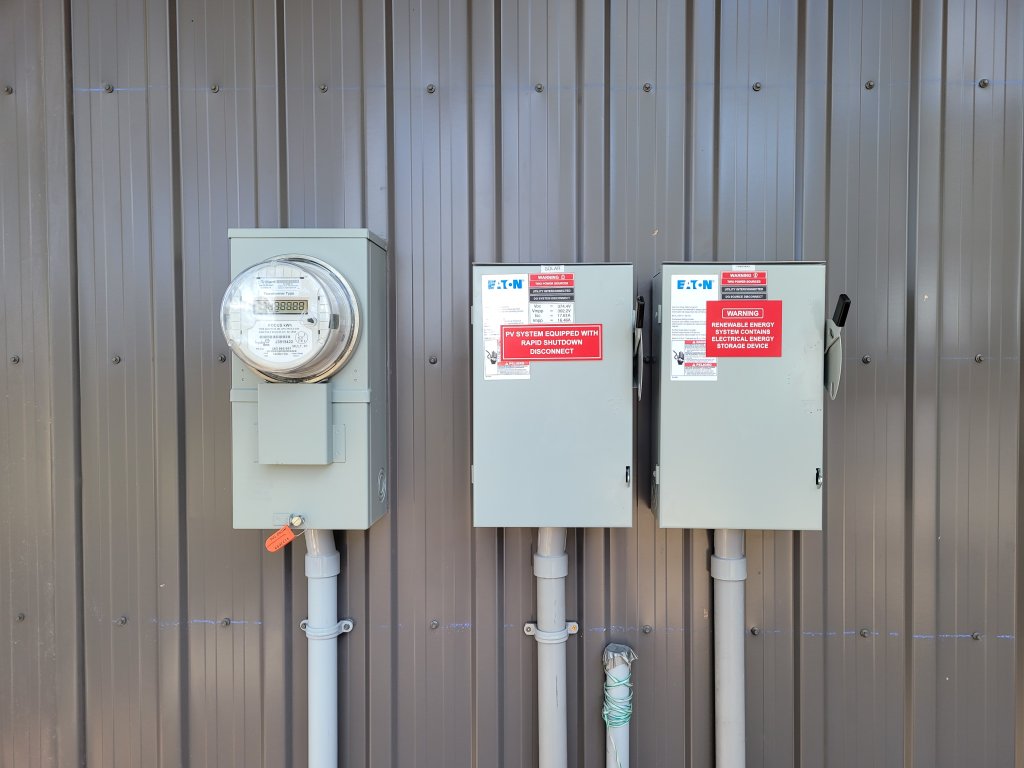
- No Panel-Level Monitoring: Traditional string inverters do not include panel level monitoring, however this can be added (optimizers) and we explain this here
- Shade and Performance Impact: If one panel in a string is shaded or underperforms, it affects the output of the entire string, potentially reducing system efficiency.
- Complex Rooftop Design: String inverters require careful consideration of rooftop layout to avoid shading issues and ensure optimal performance.
-
Optimizers: Elevating String Inverters
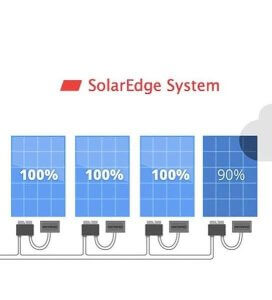 Optimizers, also known as DC optimizers, are another way to enhance the performance of traditional string inverter systems. These devices are installed at the panel level, similar to microinverters, but they work in conjunction with a central string inverter.
Optimizers, also known as DC optimizers, are another way to enhance the performance of traditional string inverter systems. These devices are installed at the panel level, similar to microinverters, but they work in conjunction with a central string inverter.
Here’s what optimizers offer:
- Panel-Level Tracking: Optimizers allow individual panel performance tracking and optimization. This feature is particularly useful when dealing with panels that might not be performing at their best due to shading or soiling.
- String Inverter Compatibility: Most optimizers can be used in combination with all string inverter solutions
- Increased Efficiency: Optimizers allow each panel to perform individually from each other, getting and increased efficiency out of the system for maximum performance
- Safety Benefits: Optimizers can shut down the DC voltage at the panel level, enhancing safety during maintenance or emergencies.
Some Disadvantages:
- More Cost: Optimizers mean there is additional equipment on the roof so this comes at a higher cost than a string inverter solution.
- More Equipment: More equipment on the roof also means more potential for equipment malfunction which can mean maintenance down the road on a system.
-
Microinverters: Energizing Each Solar Panel
Microinverters are individual inverters that attach directly to individual solar panels. They convert DC to AC energy on the roof and unlike traditional string microinverters work on a panel-by-panel basis.
Some Advantages are:
- Panel-Level Monitoring: Microinverters provide real-time monitoring of each panel’s performance, enabling you to pinpoint any issues quickly and optimize your system’s efficiency.
- Shade Tolerance: Microinverters mitigate the impact of shading. When one panel is shaded or underperforming, it doesn’t affect the output of the entire system.
- Efficiency: Microinverters optimize the energy harvest of each panel, even if some panels are shaded or dirtied.
Disadvantages are:
- More Equipment: Microinverters are more equipment than one single inverter, which can lead to more issues with the system at a later date
- Inverter on the roof: The inverter is the weakest point of a solar PV solution, and when you have an issue it’s likely to be on the roof
- Microinverter Capacity: Some panels have a higher power output than the microinverter itself, which can lead to a loss of power.

The choice between microinverters, optimizers and string inverters depends on your specific needs, budget and installation conditions. Whichever technology you choose, you are taking a significant step towards a clean and more sustainable future. At Bluewater Energy, We’re here to guide you through this process, and help you navigate these choices to ensure that you are getting the best designed solar PV system that aligns with your energy goals and needs.
If you’d like to learn more or get started on this process with us, don’t hesitate to reach out to us. We look forward to helping you!
Sign up for our Newsletter here!